AI and Data Privacy in Finance
Understanding the Crucial Role of Data Privacy in AI and Data Science within Finance
Protection of data is important more than ever. With new regulations appearing yearly such as GDPR, AI EU Act, companies need to decide how to innovate within the borders of law.
Automating complex trading strategies to personalizing banking services, AI's role in harnessing and analyzing vast amounts of financial data is undeniable. However, with great power comes great responsibility, particularly regarding the delicate balance between leveraging AI for financial advancements and ensuring robust data privacy.
This article delves into the intricate relationship between AI and data privacy in finance, highlighting the pressing challenges and regulatory frameworks that shape this dynamic field.
This article is a part of a series:
AI and Data Privacy In Finance: An Introduction
Technological Strategies and Possible Solutions
Best practices and future directions
1. Data Privacy Challenges in AI-Driven Finance
Integrating AI into financial services brings various data privacy challenges. AI systems often require access to a vast array of personal and transactional data to function effectively. This data, if mishandled, can lead to significant privacy breaches.
One of the primary concerns is the ability to infer sensitive information from seemingly non-sensitive data by using too much data, even when anonymized.
For example, an AI system analyzing spending patterns could inadvertently reveal a user's health issues or personal preferences, which are private. Another example is, an AI system could use data of spending patterns and location information such as streets and infer the user behind it.
Another challenge is the risk of data breaches. AI systems, by their nature, consolidate and analyze large data sets, making them attractive targets for cyberattacks. Financial institutions have been the targets of some of the most significant data breaches in history, where personal information of millions of customers was compromised. As AI becomes more prevalent in finance, the risk of such breaches potentially escalates, emphasizing the need for enhanced data security measures.
Moreover, AI can perpetuate biases if not carefully managed. AI algorithms are only as unbiased as the data they are trained on. If this data contains historical biases or imbalances, the AI system may inadvertently continue propagating these biases, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes. This is particularly concerning in finance, where biased AI could lead to unfair loan denials or risk assessments based on gender, race, or other personal characteristics. Decisions made in the past by humans transferred to AI systems.
Next, the evolving nature of AI technology poses a constant challenge to data privacy. AI algorithms are continually updated and improved, often with new data sets and parameters. This continuous evolution makes it difficult to establish consistent privacy controls and standards. Financial institutions must therefore remain vigilant and adaptable, ensuring that their data privacy measures can keep pace with advancements in AI technology.
In addition to these technical challenges, there is a growing concern about the legal and ethical implications of AI in finance. Regulatory bodies worldwide are striving to keep up with the rapid development of AI technologies, often lagging behind in creating frameworks that adequately address these new privacy challenges. This regulatory uncertainty creates a complex environment for financial institutions, which must navigate an evolving landscape of compliance requirements while leveraging the benefits of AI.
Another aspect to consider is the public perception and trust in AI-driven financial services. Privacy concerns can lead to mistrust and reluctance among customers to embrace AI-powered financial solutions. Financial institutions, therefore, face the dual task of not only ensuring data privacy compliance but also building and maintaining customer trust by demonstrating their commitment to protecting personal information.
So as recap: As AI continues to transform the finance sector, the challenges regarding data privacy are multifaceted and continually evolving. Financial institutions must address these challenges head-on, through robust data protection measures, ethical AI practices, and compliance with regulatory standards. Only by doing so can they harness the full potential of AI in finance while safeguarding the privacy and trust of their customers.
I know that are a lot of challenges, but it is worthy. In the next articles I‘ll share some tip and tricks to manage the risk within the company, so subscribe to not miss any future article.
2. Regulatory Landscape for AI and Data Privacy
Navigating the regulatory landscape is crucial for financial institutions leveraging AI. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States are two significant regulatory frameworks that impact how financial data is handled. These regulations mandate stringent consent requirements, data subject rights, and penalties for non-compliance, shaping how financial data is collected, processed, and stored.
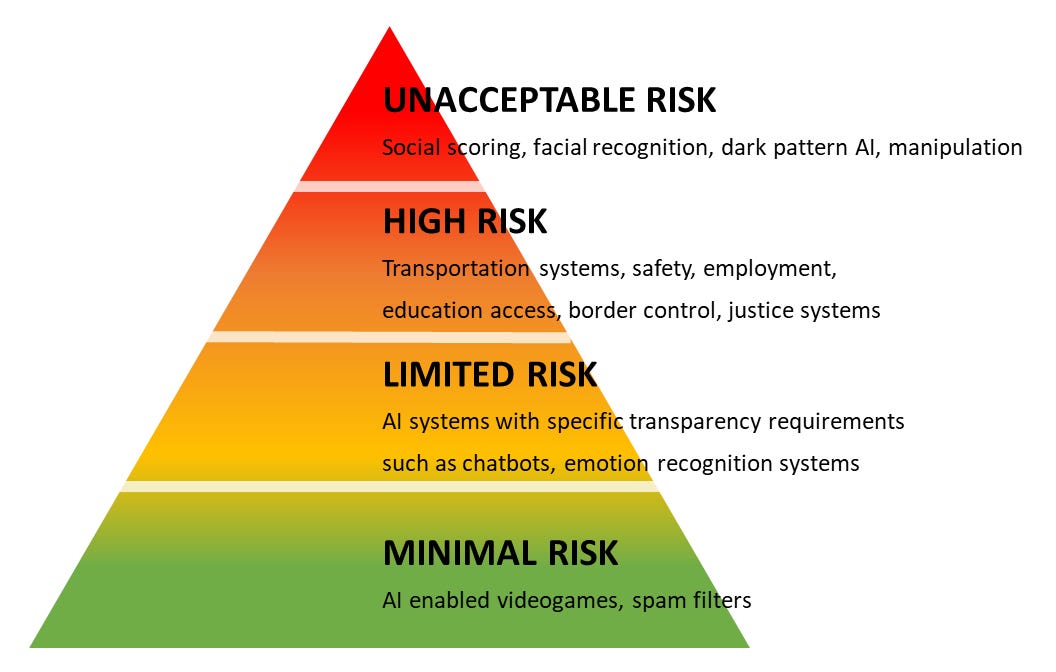
Recently, the European Union has proposed the Artificial Intelligence Act, a new regulatory framework specifically targeting AI systems. The AI Act classifies AI applications into risk categories, with the highest-risk categories, including those used in critical infrastructure and that affect fundamental rights, subject to strict compliance requirements.
For the finance sector, this could mean rigorous testing, documentation, and transparency requirements for AI systems, especially those involved in credit scoring, risk assessment, and other critical functions.
Compliance with these regulations requires financial institutions to not only protect customer data but also ensure transparency in how AI algorithms make decisions. This is particularly challenging given the often 'black box' nature of AI, where the decision-making process is not always clear, even to the developers of the algorithm.
The intersection of AI and data privacy regulations, particularly the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the proposed EU AI Act, presents a complex landscape for data scientists in the finance sector. These regulations profoundly impact how AI systems are developed, deployed, and managed.
The bottom line: Innovate but just with care and managed!
Impact of GDPR on AI and Data Science
The GDPR, introduced in 2018, has significantly influenced the field of AI and data science. The regulation focuses on strengthening individuals' rights over their personal data and imposes stringent requirements on how organizations collect, process, and store such data. Key aspects of GDPR that affect AI in data science include:
Lawful Basis for Data Processing: GDPR requires a legal basis for processing personal data, such as explicit consent from the data subject, which needs to be specific and informed.
Data Minimization and Purpose Limitation: AI systems should collect and process only the data necessary for their intended purposes and restrict processing to those purposes.
Profiling and Automated Decision Making: GDPR imposes restrictions on profiling and automated decision-making, requiring transparency and an opportunity for individuals to opt out. This impacts how data scientists develop and deploy models that make automated decisions based on personal data.
Consent and Transparency: When personal data is processed for purposes other than legitimate business interests, explicit consent is required. GDPR also necessitates clear and understandable language in explaining data processing to individuals, which challenges data scientists to communicate complex AI processes in simpler terms.
Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs): GDPR mandates DPIAs for AI applications that pose significant risks to individuals' rights, helping identify and mitigate potential data protection risks.
Anonymization and Pseudonymization: These techniques are emphasized to enhance privacy in AI systems that process personal data.
Security and Accountability: GDPR requires organizations to ensure the security of personal data and be accountable for their data processing activities.
The GDPR principles of fairness, transparency, accuracy, and accountability are central to the ethical use of AI in data science, promoting a more regulated and trusted data market.
Possible Impact of the EU AI Act on Data Science
The proposed EU AI Act aims to regulate the development and use of AI systems, ensuring they are transparent, reliable, safe, and respect fundamental rights. This Act represents one of the first comprehensive global AI laws and could significantly impact data science in several ways:
Risk Assessment: Data scientists will need to assess the risk level of their AI products and develop them according to the corresponding regulations.
Transparency and Reliability: The AI Act emphasizes the need for AI systems to be transparent and reliable. This may require data scientists to implement mechanisms that enhance the explainability of AI decisions and ensure the systems are robust and free from biases.
Safety and Fundamental Rights: The AI Act focuses on ensuring AI systems respect fundamental rights, which might lead to additional compliance requirements for AI applications in finance.
In conclusion, the GDPR and the proposed EU AI Act represent significant steps in regulating the intersection of AI and data privacy. For data scientists, these regulations necessitate a careful approach to AI development and deployment, ensuring compliance with data privacy laws while leveraging AI's potential in the finance sector.
It is a collaborative task between Data scientists, Data Protection Officers, Risk Managers and Lawyers.
Let me know down in the comments what do you think about GDPR and the EI AI Act.
3. Conclusion
AI and data privacy in finance is a complex and evolving issue. As financial institutions increasingly adopt AI to enhance their services, the need to address the accompanying data privacy challenges becomes more critical. Regulatory frameworks like GDPR, CCPA, and the AI Act in the EU play a crucial role in shaping how financial data is handled and protected. However, compliance alone is not enough. Financial institutions must proactively adopt strategies that ensure data privacy at the forefront of their AI initiatives. This includes investing in robust cybersecurity measures, ensuring transparency and fairness in AI algorithms, and fostering a culture of privacy awareness and responsibility. By striking the right balance between leveraging AI's potential and protecting individual privacy, the finance sector can continue to innovate responsibly and sustainably in the digital age.